프로세스와 스레드
📚 기본 개념 정리
먼저 핵심 개념들을 정리해보겠습니다:
- program: 컴퓨터가 실행할 수 있는 명령어의 집합
- process: 실행중인 프로그램(독립된 메모리를 할당받음)
- CPU: 명령어를 실행하는 연산장치
- Main Memory: 실행 중인 프로그램과 데이터가 저장되는 주기억장치
- Ready Queue: 메모리에 있는 프로세스들 중 CPU 할당을 기다리는 프로세스들의 논리적 대기줄
- I/O (input, output): 파일을 읽고 쓰기, 네트워크, 입출력 장치
- Process Manager: 이 둘을 연결하고 관리하는 스케줄러
시스템 아키텍처
현대 컴퓨터 시스템은 크게 3개 계층으로 구분됩니다:
graph TD
subgraph User ["User Space"]
A[Program<br/>컴퓨터가 실행할 수 있는<br/>명령어의 집합]
B[Process<br/>실행중인 프로그램<br/>독립된 메모리 할당]
end
subgraph Kernel ["Kernel Space"]
C[Main Memory<br/>실행 중인 프로그램과<br/>데이터가 저장되는 주기억장치]
G[Ready Queue<br/>CPU 할당을 기다리는<br/>프로세스들의 대기줄]
F[Process Manager<br/>프로세스 스케줄링<br/>메모리 관리]
end
subgraph HW ["Hardware (H/W)"]
D[CPU<br/>명령어를 실행하는<br/>연산장치]
E1[SSD<br/>빠른 저장장치]
E2[HDD<br/>대용량 저장장치]
E3[Network<br/>네트워크 장치]
E4[I/O Devices<br/>키보드, 마우스, 모니터]
end
%% User Space 내부 관계
A -->|실행| B
%% User Space와 Kernel Space 간 시스템 콜
B <-->|System Call| F
B <-->|메모리 로드| C
%% Kernel Space 내부 관계
C <-->|프로세스 정보| G
F <-->|큐 관리| G
%% Kernel Space와 Hardware 간 관계
F <-->|스케줄링| D
G <-->|다음 프로세스 선택| D
C <-->|명령어 fetch/execute| D
F <-->|I/O 제어| E1
F <-->|I/O 제어| E2
F <-->|네트워크 제어| E3
F <-->|장치 제어| E4
%% 계층 구분선 스타일
classDef userLayer fill:#e8f5e8,stroke:#2e7d32,stroke-width:3px
classDef kernelLayer fill:#fff3e0,stroke:#f57c00,stroke-width:3px
classDef hwLayer fill:#fce4ec,stroke:#c2185b,stroke-width:3px
classDef userElement fill:#c8e6c9,stroke:#388e3c,stroke-width:2px
classDef kernelElement fill:#ffcc02,stroke:#f57c00,stroke-width:2px
classDef queueElement fill:#fff9c4,stroke:#f9a825,stroke-width:2px
classDef hwElement fill:#f8bbd9,stroke:#c2185b,stroke-width:2px
class A,B userElement
class C,F kernelElement
class G queueElement
class D,E1,E2,E3,E4 hwElement
📈 프로세스 실행 방식의 진화
1. 단일 프로세스 (Single Process)
특징:
- 한 번에 하나의 프로그램만 실행
- CPU가 하나의 작업을 완료할 때까지 다른 작업 불가
- 초기 컴퓨터 시스템의 방식
문제점:
- I/O 작업 중에 CPU가 놀고 있음
- 전체적인 시스템 효율성이 매우 낮음
graph LR
subgraph System ["단일 프로세스 시스템"]
P1["P1<br/>프로세스"]
CPU["CPU"]
end
subgraph Timeline ["시간축 →"]
T1["P1"] --> Gap1["⏸️<br/>I/O대기"] --> T2["P1"] --> Gap2["⏸️<br/>I/O대기"] --> T3["P1"] --> Gap3["⏸️<br/>유휴"] --> T4["P1"] --> More["..."]
end
P1 -.-> CPU
CPU -.-> T1
%% 연결선으로 실행 흐름 표시
T1 -.-> T2
T2 -.-> T3
T3 -.-> T4
%% 스타일링
classDef process fill:#ff9999,stroke:#ff6666,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef cpu fill:#ffff99,stroke:#ffcc00,stroke-width:3px,color:#000
classDef running fill:#66ff66,stroke:#00cc00,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef waiting fill:#cccccc,stroke:#999999,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef system fill:#f0f0f0,stroke:#999,stroke-width:1px
classDef timeline fill:#e6f3ff,stroke:#4db6e6,stroke-width:2px
class P1 process
class CPU cpu
class T1,T2,T3,T4,More running
class Gap1,Gap2,Gap3 waiting
class System system
class Timeline timeline
2. 멀티프로그래밍 (Multiprogramming)
특징:
- 메모리에 여러 프로그램을 동시에 적재
- 하나의 프로그램이 I/O 대기 시 다른 프로그램 실행
- CPU 활용률 향상이 주목적
장점:
- CPU 유휴 시간 최소화
- 전체적인 시스템 처리량 증가
문제점:
- 한 프로세스가 CPU를 독점할 수 있음
- 응답성 보장이 어려움
graph LR
subgraph System ["멀티프로그래밍 시스템"]
P1["P1<br/>프로세스"]
P2["P2<br/>프로세스"]
CPU["CPU<br/>(하나)"]
end
subgraph Timeline ["시간축 →"]
T1["P1"] --> T2["P2"] --> T3["P1"] --> T4["P2<br/>📏📏📏📏📏<br/>너무 길어짐!"] --> T5["P1<br/>⏳대기"] --> T6["P2<br/>📏📏📏<br/>계속..."] --> More["❌<br/>문제!"]
end
%% 프로세스에서 CPU로의 연결
P1 -.-> CPU
P2 -.-> CPU
CPU -.-> T1
%% 스타일링
classDef process1 fill:#ff9999,stroke:#ff6666,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef process2 fill:#99ccff,stroke:#6699ff,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef cpu fill:#ffff99,stroke:#ffcc00,stroke-width:3px,color:#000
classDef system fill:#f0f0f0,stroke:#999,stroke-width:1px
classDef timeline fill:#e6f3ff,stroke:#4db6e6,stroke-width:2px
classDef problem fill:#ffcccc,stroke:#ff0000,stroke-width:3px,color:#000
class P1 process1
class P2 process2
class CPU cpu
class T1,T3 process1
class T2,T4,T6 process2
class T5 process1
class More problem
class System system
class Timeline timeline
3. 멀티태스킹 (Multitasking)
특징:
- 시분할(Time Sharing) 방식으로 CPU 시간을 나누어 할당
- 매우 짧은 시간 단위(퀀텀)로 프로세스들을 번갈아가며 실행
- 사용자에게는 동시 실행처럼 보임
장점:
- 공정한 CPU 시간 분배
- 뛰어난 응답성
- 대화형 시스템 구현 가능
단점:
- 컨텍스트 스위칭 오버헤드 발생
graph LR
subgraph System ["멀티태스킹 시스템"]
P1["P1<br/>프로세스"]
P2["P2<br/>프로세스"]
CPU["CPU<br/>⏰ 타이머"]
end
subgraph Quantum ["퀀텀 (Time Slice) →"]
Q1["P1<br/>10ms"] --> Q2["P2<br/>10ms"] --> Q3["P1<br/>10ms"] --> Q4["P2<br/>10ms"] --> Q5["P1<br/>10ms"] --> Q6["P2<br/>10ms"] --> Q7["P1<br/>10ms"] --> Q8["P2<br/>10ms"] --> More["..."]
end
subgraph UserView ["👁️ 사용자가 보는 것"]
Concurrent["P1과 P2가<br/>🤝 동시에 실행되는<br/>것처럼 보임!"]
end
%% 연결
P1 -.-> CPU
P2 -.-> CPU
CPU -.-> Q1
%% 사용자 관점 연결
Quantum -.-> UserView
%% 스타일링
classDef process1 fill:#ff9999,stroke:#ff6666,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef process2 fill:#99ccff,stroke:#6699ff,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef cpu fill:#ffff99,stroke:#ffcc00,stroke-width:3px,color:#000
classDef system fill:#f0f0f0,stroke:#999,stroke-width:1px
classDef quantum fill:#e6f3ff,stroke:#4db6e6,stroke-width:2px
classDef user fill:#e8f5e8,stroke:#66cc66,stroke-width:2px
class P1 process1
class P2 process2
class CPU cpu
class Q1,Q3,Q5,Q7 process1
class Q2,Q4,Q6,Q8 process2
class More process1
class System system
class Quantum quantum
class UserView user
class Concurrent user
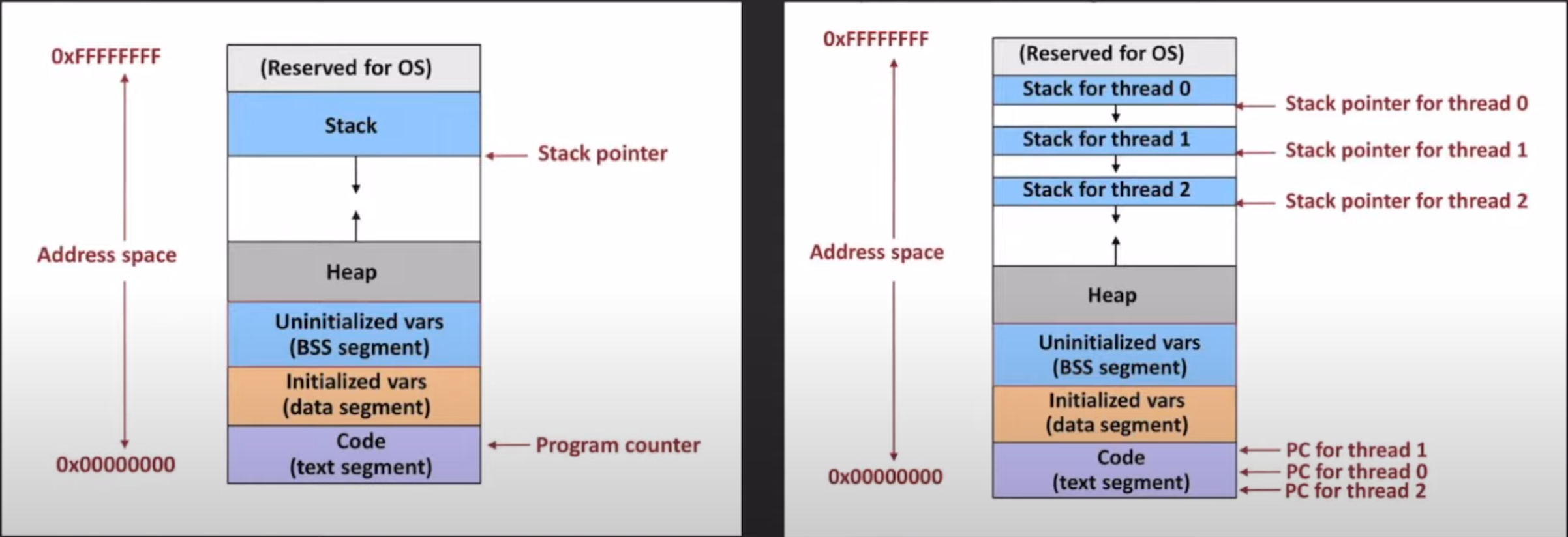
4. 멀티스레딩 (Multithreading)
특징:
- 하나의 프로세스 내에서 여러 실행 흐름(스레드) 생성
- 메모리는 공유하지만 실행 스택은 독립적
- 진정한 병렬 처리 가능 (멀티코어 환경)
장점:
- 실제 동시 실행
- 메모리 공유로 효율적인 통신
- 빠른 컨텍스트 스위칭
단점:
- 동기화 문제 발생 가능
- 프로그래밍 복잡도 증가
graph TD
subgraph System ["멀티스레딩 시스템"]
subgraph Processes ["프로세스들"]
subgraph P1_Block ["프로세스 P1"]
T1_1["스레드 T1-1"]
T1_2["스레드 T1-2"]
end
subgraph P2_Block ["프로세스 P2"]
T2_1["스레드 T2-1"]
T2_2["스레드 T2-2"]
end
end
subgraph CPUs ["CPU 코어들"]
CPU1["CPU1<br/>⚡ 코어1"]
CPU2["CPU2<br/>⚡ 코어2"]
end
end
subgraph Execution ["실제 실행 (동시에!)"]
E1["CPU1: T1-1 실행"]
E2["CPU2: T2-1 실행"]
E3["CPU1: T1-2 실행"]
E4["CPU2: T2-2 실행"]
end
%% 스레드-CPU 연결
T1_1 --> CPU1
T2_1 --> CPU2
T1_2 -.-> CPU1
T2_2 -.-> CPU2
%% 실행 연결
CPU1 -.-> E1
CPU2 -.-> E2
CPU1 -.-> E3
CPU2 -.-> E4
%% 스타일링
classDef process1 fill:#ffebee,stroke:#f44336,stroke-width:2px
classDef process2 fill:#e3f2fd,stroke:#2196f3,stroke-width:2px
classDef thread1 fill:#ff9999,stroke:#ff6666,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef thread2 fill:#99ccff,stroke:#6699ff,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef cpu fill:#ffff99,stroke:#ffcc00,stroke-width:3px,color:#000
classDef execution fill:#f3e5f5,stroke:#9c27b0,stroke-width:2px
class P1_Block process1
class P2_Block process2
class T1_1,T1_2 thread1
class T2_1,T2_2 thread2
class CPU1,CPU2 cpu
class E1,E2,E3,E4 execution
Single vs Multi thread
댓글남기기